EARLY WARNINGS MANAGEMENT (EWM)
“It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to change”
-Charles Darwin.
Nexoft has introduced a new generation of IT-Solution and consultancy methodologies, called Early Warning Management (EWM).
The objective of the EWM, is by examining a very big number of parameters to alert the Managers that something (like Sales) which up to now seems normal (normality) has entered in a deterioration path, or something which is in bad condition (decline) has entered an improvement path and to follow the trajectory of this path. First important set of this methodology is the Sales of any organization. In summary EWM is able to:
When in normality:
- Detect incoming threats which can cause sales to decline, or create problems with the customers.
- Detect incoming opportunities, which, if properly exploited, can lead to better sales outcome, improved relations with the customers and great competitive advantage. When in decline:
When in decline:
- Detect conditions which can prove that the policies which have been adopted could lead to improvements of sales.
- Detect that is getting out of the decline or crisis period.
In all situations:
- Establish a unique control point for all information, and procedures, transparent to the management, which will allow a better organization of the Sales and Marketing.
- Support the decision making process and any action plan for a threat or an opportunity.
EWM can be used to analyze the whole Organization, or independently used for some Business Units or some product families.
Introduction
Sales are one of the most important and complex processes for the survival and prosperity of an organization. For an Organization, sales decline is among the most serious threats, not mentioning sales plundering becoming the worst nightmare. Sales are the most exposed part of an organization in today reality. Have some unique characteristics complete different from any other operations (which have some kind of stability).
- It is dispersed in greater geographical area among different environments and cultures.
- In reality each customer is a unique variable in continuous change.
- It is multilevel operation, with each level with very different tasks but all interconnected (back-office, salespeople, marketing, representatives, agents, transport etc.).
- Sales are influenced in the daily operations from other operations (production, planning, quality, financial).
- Sales influence the organization more than any other operation.
Today we are not in days of normality. Today we experience working and living in a volatile, global and highly competitive environment, where the normality rules of the past are not valid anymore. In present times, every company encounters fast moving, complex interactions with the external and/or the internal environment, which in turn stress and cause continuous organization’s performance variations.
As a result Sales operation is very difficult to be controlled and balanced.
Some of these variations are averaged in time and actually do not cause any harm. Nevertheless, there are certain changes which are accumulated underneath, taking momentum, generating other events and finally, after a certain incubation period, reach a point where the organization is under serious threat.
Such a negative result cannot happen all of a sudden. For this result there several causes. As aforementioned, during incubation period certain factors have passed unnoticed or someone detected them, but no action has been taken. Sales are brought down by the accumulative result of many factors not properly identified and treated. Under this sense, sales drop is not the primary cause but undoubtedly the mere effect of other factors.
This situation becomes more complex in the modern manufacturing organizations which manage many Business Units, each one oriented to different market sectors with many different product families, each one presenting different dynamics.
Present volatile environment is not only threats. Several windows of opportunities may appear, but must be detected and explored for exactly the same reasons to the threats.
Nexoft has developed a new generation of IT-Solution and consultancy methodologies which is called Early Warning Management (EWM). Now managers are allowed to detect incoming threats which will result in sales decline, detect opportunities which ought to be explored in order to increase sales, support the decision making process, support the platform for action and provide a common repository of all the information related to sales and the customers, transparent for the management. It is a new generation of IT-Solution which uses Logic, Rules and Intelligence to scan all the available information. Incoming threats and opportunities are identified. Implementation of such a system, will offer to the Top Management as well as to the sales department and other related departments (quality, production, purchasing, financial) a very high level of knowledge, understanding and control of sales related operations. Competitiveness of the whole organization in the market is then increased.
The Theory
- We define a threat as a situation caused from a series of events which - when will be materialized - will stress the organization Values and its progress. Threats are contra-survival
- We define an opportunity as a situation caused from a series of events which - when will be materialized and exploited - will benefit the organization Values and its progress. Opportunities are pro-survival
- A threat or an opportunity is composed from the state of many individual factors
- Each factor is composed from a finite number of parameters
One of the worst threats of any organization is the drop in sales (quantitatively or profit-margin wise). Decrease in sales will influence also other important Values of the company.
Today, when an organization observes a decline in Sales, it means that the threat has already been materialized. But this did not happen in a moment; it took time.
The threat is an effect (result) of many underlined causes which have passed undetected or untreated. At some point in time, they reach a momentum and so the threat becomes evident by the normal control tools (standard reports). In other words, a threat has certain dynamics as time progresses, until is visible from the decision levels (Management) of an organization. During this process, it leaves a lot of “footprints”. If these “footprints” are not detected or no corrective actions are taken by the organization the threat is materialized and then is transformed to danger. At that point, the organization is facing a crisis. The organization is stressed and will need a considerable amount of time and effort to remediate this situation, not mentioning that and there is a high probability, in the end of this cycle, the organization will be harmed.
In the following diagram, a common profile of an incoming threat is presented.
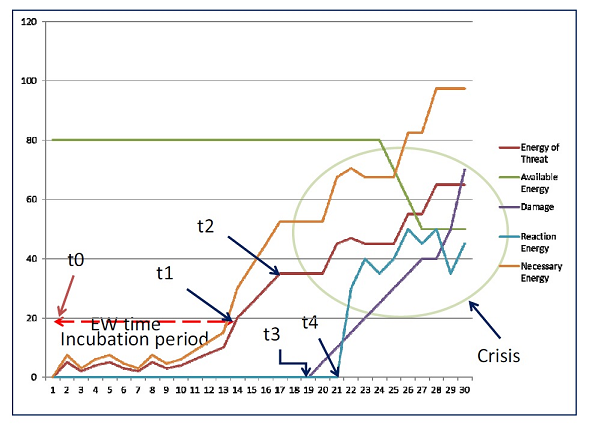
Any incoming threat has its own dynamics (energy of threat) which starts from small events - most likely pass unnoticed - but over the time accumulates momentum. In the diagram this is the period between the (t0) until (t1) and is called Incubation period.
At a certain moment (t1) the threat is detected inside the organization, but not from the Management. This is because some people within the organization are closer to the real events; they have the knowledge and the expertise to realize the meaning of the events. Analyzing major crises in an organization has clearly proved that some people inside knew or felt what was coming. It is the inherent difficulty to present such a threatening situation with sound arguments, proving that there is an issue which immediately needs the company’s attention or the lack of some clear communication lines.
As the energy of threat becomes greater, it is finally detected from the Management (t2). But even then at point (t2), an action cannot be taken until the moment (t4). The reason of this delay is the required time for a danger assessment plus the time needed to find and decide the actions to follow. The actual magnitude of this delay depends on the preparedness and responsiveness of the organization. From that moment on, the organization faces a CRISIS.
As time progresses the threat may continue to grow and it is highly probable to act as a trigger to other problems affecting different sections inside the organization. In other words, there is a chain reaction situation, where a threat (effect) will become the origin (cause) of another threat. It is obvious that in this case the situation happens to be more difficult to manage.
An example of a chain reaction is a situation where the company’s sales are falling. As a result, the profits of the company will fall, so as the worth value of its stock. Furthermore, this could lead to problems in company’s relations with the banks, several rumors in the market, and changes in terms with the suppliers and internal conflicts. This is due to the fact that important aspects involved in a organization operations (Organization Values) are interconnected and interdependent.
Looking at the diagram, other important lines in the Threat Dynamics graph are the Available Energy (green line) of the company to spend in order to solve the problem and the Necessary Energy (orange line) to annihilate a threat. During incubation period, the Available Energy of the organization is high, whereas the Necessary Energy to solve a threat is relative small. In other words, if small efforts are put in, the danger can be annihilated. This is not the case as danger accumulates momentum from (t1→) onwards. As time progresses, the Energy of the Threat (purple line) is increasing, while the Necessary Energy is also increasing. So, in order to confront the threat, the company should consume a bigger part of its Available Energy.
The financial damages can start at any moment (t3). From the moment that an organization will start having financial bleeding due to a threat, the threat has an impact on the organization. So the (t3) point is called impact moment. The losses indicated in the diagram, are the primary financial loses which can be measured by the organization. In reality, except these loses there are other secondary ones which will appear later in time, as well as collateral damages in intangible assets like loss of reputation, loss of important personnel, conflicts in various levels etc. The list is long and none of these can be presented in conventional financial forms.
The circle in the graph represents a crisis situation where the environment is very complex and strongly non-linear. This implies that crises are difficult to manage, and the time required to be resolved it is usually too long. During this time, the organization is severely stressed and damaged, might enter a decline period and finally risk its survival.
Under this notion, it is much better and obviously more important to spend time in detecting and annihilating possible threats BEFORE they form a serious peril. The energy, then, needed to correct is always smaller than the one required when they have acquired momentum and magnitude.
This principle is an important point, the managers in an organization must understand.
The Solution
The methods, procedures and functionalities which allow the detection during the incubation period and the neutralization of incoming threats are called Early Warnings Management (EWM) and constitute an enormous knowledge extension for the organization.
To be able to implement an Early Warnings Management methodology the following prerequisites are necessary:
- Focus attention to certain factors or certain changes
- Detect incubation of threats at the earliest time possible
- Communicate fast to the Decision Levels
- Assess the qualitative and the quantitative characteristics of the threat
- Understand the available resources and the resilience of the organization.
- Be Prepared to manage such cases and able to decide fast
Such an implementation methodology can be done only in a new IT manner, as the available conventional systems are not capable of providing this methodology and functionality.
But it is not only an issue of information systems capabilities. It is absolutely crucial that the organization needs to be trained to think and act in a different manner. It needs to be able to identify and distinguish certain important factors, which normally will have passed unnoticed or with no reaction. This increased consciousness will lead to a better understanding of the reality and develop a new participation and communication mode. In a few words, a completely new culture will emerge, providing the organization with the greatest competitive advantage.
Nexoft has clearly realized these necessities and has developed a series of Consultancy methodologies and IT-Tools, in order to provide the organizations with these advanced functionalities.
The detection of a threat is done with two methods:
- An incoming threat in phase of incubation is recognized from the “footprints” is leaving. These footprints are separated in two categories. The symptoms, meaning negative changes which are happening in some operation factors and the organization can detect and measure by itself and the signs, meaning again negative changes which are not detectable from within the organization but from the external environment (customers, suppliers, collaborators etc.)
- For threat factors which cannot be detected explicitly, we use the deviation from the normal scene (DNS). The deviation from normal scene is a very powerful multipurpose tool which allows the management to define what they consider as Normal Operation of the organization (a very important concept by itself) and to follow up deviations from this normality. This method does not have the prevention capability of the first method, because it cannot look to the primary causes of the problem. Instead, it detects the problem at a later stage, where the company has started to be affected by the threat. Due to the fact that such controls of normality can be done frequently, they are included in the Early Warnings Management methodology. DNS is the most suitable method to use when the company has already been impacted by a threat (facing a crisis) because it describes very well the dynamics of the organization. The reason is that this method is capable of presenting the resilience of the company and at the same time the damage the company has already suffered. In other words, it is a powerful tool in the decision making process. The main functionality of this method is explained in the Operational Plan and Industrial Costing Introduction.
Concerning the detection of incoming threats for the sales of an organization, we have determined a number of symptoms and signs which operate as factors to cause a threat materialization and can provoke the fall or collapse of sales.
Some of these factors are summarized in the table 1 shown at the end of this text.
All these factors are analyzed for every Business Unit and every product family for the current period and will be compared to the respective results of previous periods, in order to find incoming threat. Some of the factors (like lost customers) are explicit event of a threat, while others are detected as threat only by examining the trends from previous periods or the power level of the factor.
The System
EWM is based on efikton® a modular OPEN platform.
EWM is integrable to the main systems of the company to use the information, which already exist inside the organization. In case that any of the above group of information is not available in the organization, EWM can manage the missing information autonomously.
For each BU/Product Family the customer defines the factors and the factors’ parameters which need to be examined. The system is open to define new factors and new parameters.
These parameters are categorized as follows:
- Original parameters come from the existing data (e.g. Nr of Delivery Orders, Quantity, Value, Nr. of complains, Nr. of Open Claims). The EWM will collect automatically all these parameters’ value for a given time period.
- Derivative parameters derived from the Original Parameters (e.g. Average Value/Quantity for sales orders, Quantity of Claims/Quantity Shipped.
- Trends which show the parameter compared to other time periods (e.g. Trend Month, Moving Averages, etc.).
- Alarms and alerts for Threats and Opportunities.
The result will be a comprehensive situation showing if there are factors which act in a non-desirable or extraordinary way and need attention. The management of the organization will know where to focus their attention and where to spend the resources for small corrective actions.
The system will support examination or corrective activities for each of these parameters, so the Management will have full control and follow up on these corrective actions.
Also the system will be very useful in the case that the organization faces a Crisis because of sales (either in a decline or a plundering). With the EWM, it will be able to follow up in close look any improvement or further deterioration related to the initiatives that have been applied. Because before we see an improvement in sales we have to see the improvement in some factors. This will give to the organization an early indication that these initiatives have a positive effect.
The implementation of Early Warnings methodologies and solutions will certainly bring advantages to the whole of the organization structure like:
- Better understanding the reality
- Better Participation
- Better Communication through the Company Levels
- Better Collaboration between the different departments, since the impact of one department’s activity will be clear
- Better Preparation and Responsiveness
- Faster Reaction to the problems and opportunities
All of the above lead towards a new, more competitive THINKING
Efikton®-EWM it is not an isolated, stand-alone system, but actually part of a much broader Management System offering expertise solution modules in the areas of Production Control, Quality Control, Production Planning, Products Development, CRM, Sales and Inventory Analysis, Innovation Management and Continuous Improvement, Managing Collaboration Processes with Customers and Suppliers, Operational Plan and Industrial Costing.